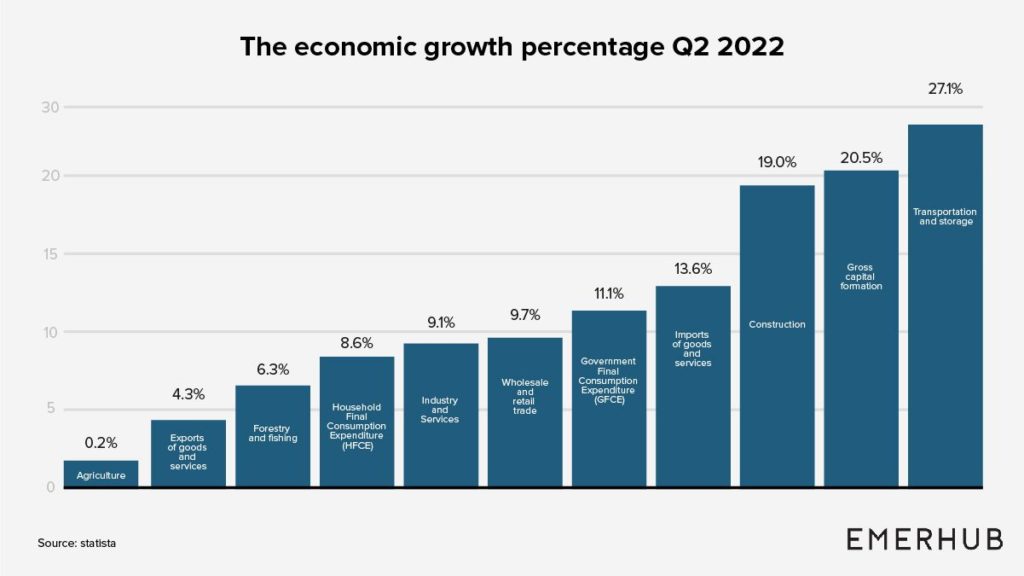
After the pandemic, the Philippine economy is prepared to make up ground and return to its pre-pandemic growth rate. The loosening of pandemic-related restrictions has led to a post-year-on-year GDP (GDP) increase of 8.2 percent in the first quarter of 2022 and 7.4 percent during the 2nd quarter of 2022.
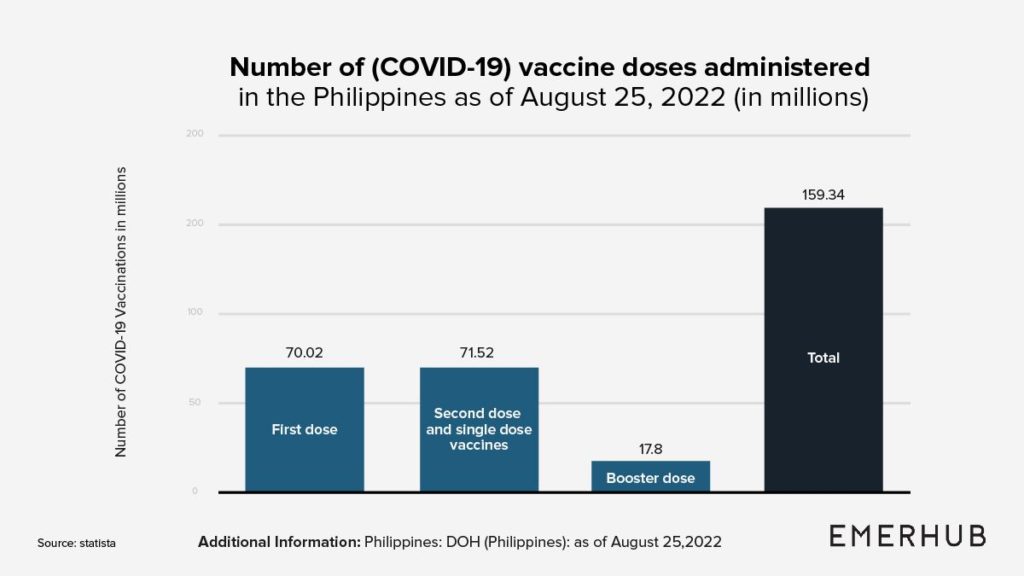
The forecast for the coming years includes various factors that impact the overall growth of GDP. ADB and the World Bank forecast strong GDP growth due to the rising rates of vaccinations, a decrease in COVID-19-related infections, and the normalization of business activity.
The return of foreign investment is expected to contribute to the Philippines’ economic recovery, especially following the introduction of changes in the legislation in the Public Service and Foreign Investment Acts in March 2022. These amendments are designed to increase FDI by permitting foreigners to create and own 100% of domestic businesses. It also reduces the minimum amount of employment and paid-in capital (for specific technologies).
The Philippines has also been affected by the possibility of a growing interest rate in the US and other countries. This has reduced the Peso exchange rate and raised the cost of imports. After reports that Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas (BSP) might adopt an approach that is more relaxed in combating inflation, the BSP tightened its benchmark rate to 75 basis points on the 14th of July and brought it up to 3.25 percent. Many analysts anticipate the rate rising to 4.5 percent by the end of the year (still lower than the record high of 4.75 percent).
The economy expanded by 8.2 percent in the initial quarter of the year. The forecast is for 6-6.5 percent growth this year and in the next. The government plans to put in place structural reforms and provide more opportunities that will help the economy grow by 8 percent between 2023 and 2028.







