Table of contents
Vietnam is gradually becoming a more open economy. In this article, we will list Vietnam trade agreements as well as take a look at some of the limitations Vietnam has lifted on foreign investment over the past few years.
This article was last updated in March 2019.
New opportunities for foreign investors in Vietnam
Although most business lines were already open to foreign ownership, investors still faced restrictions in some industries until 2017. This made obtaining the investment license and business registration certificate time-consuming and complicated.
However, in September 2017, the Ministry of Industry and Trade issued Decision No. 3610a/QD-BCT whereby over 600 restrictions were removed, creating a lot of business opportunities and making doing business easier for foreign investors.
Furthermore, in October 2018, the Ministry of Industry and Trade issued Decision No. 3720/QD-BCT which will gradually remove or simplify over 200 other business conditions throughout 2019-2020.
Examples of some of the eased restrictions:
|
Field |
Lifted regulations |
|
Food safety |
Food safety regulations were eased for small businesses, e.g., household businesses, hotel restaurants, street food businesses |
|
Liquor trading |
The population of the area where the liquor trading enterprise operates no longer limits the number of liquor trading permits |
|
Cigarette trading |
Imported tobacco no longer needs to bear the stamps of tobacco import issued by the Ministry of Finance |
|
Electricity wholesale and retail |
Conditions on professional qualifications of direct operators in electricity wholesale and retail activities together with conditions on electricity import permits and requirements for other electricity activities were reduced |
|
E-commerce |
A valid domain name when setting up an e-commerce website for sales and services is no longer required |
|
Multi-level sales business |
Conditions related to goods were reduced. E.g., goods no longer have to comply with the multi-level sales company’s enterprise registration certificate or the investment certificate. However, businesses have to notify the Ministry of Trade and Industry. |
Vietnam trade agreements
In 2007, Vietnam became a member of the World Trade Organization (WTO) and has later enforced numerous trade agreements, either as a member of ASEAN or separately, to liberalize trading and economic activities with several states.
#1 ASEAN Free Trade Agreement
Vietnam is a member of the ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA) which aims to support local production within ASEAN member states. This means that import taxes for certain products imported from other ASEAN countries vary between 0-5%. However, note that most of these goods are free from import tax.
Some of these products are:
- Livestock
- Vegetables
- Agricultural machinery
- Meat and fish
- Dairy products
#2 ASEAN-Australia and New Zealand Free Trade Agreement (AANZFTA)
ASEAN, Australia and New Zealand signed the AANZFTA on February 2, 2009, and it was enforced on January 1, 2010.
AANZFTA aims to facilitate economic and trade activities between Australian and New Zealand investors and Vietnam. The current tariff schedule, detailed in Decree 158/2017/ND-CP, is effective from 2018-2022.
By 2018, 86% of the tariff lines were exempt from tax, including:
- Confectionery
- Garment and garment accessories
- Computers, electronic products, and accessories
- Corn
- Machines and equipment
Moreover, the goal is to abolish import tax on 92% of the products imported to Vietnam under AANZFTA by 2022.
#3 ASEAN-India Free Trade Area (AIFTA)
In 2003, ASEAN and the Republic of India signed the Framework of Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement (CECA) and the final agreement in 2009. The AIFTA took effect on January 1, 2010.
Consequently, Vietnam has set specific import tariff schedule for India for the period of 2018-2022, as stated in Decree 159/2017/ND-CP.
In 2018, 59% of the tariffs were eliminated and by 2024, Vietnam aims to cut import taxes on 80% of the products imported from India.
#4 ASEAN-Japan Comprehensive Economic Partnership (AJCEP)
The ASEAN-Japan Comprehensive Economic Partnership (AJCEP) was signed and enforced in 2008. This Partnership covers trade in goods and services, investment, and economic cooperation.
Vietnam announced the special preferential import tariff schedule 2018-2023 for Japanese exporters in Decree 160/2017/ND-CP.
By 2018, Vietnam abolished taxes on 62.2% of the total product lines, including:
- Plastic materials and chemicals
- Machinery and equipment
- Tools and spare parts
- Computers and electronic products
- Various textile materials
- Medicine
Furthermore, the percentage will rise to 88.6% of the whole tariff list by 2025.
#5 ASEAN-China Free Trade Area (ACFTA)
The initial framework was signed in 2002, however, the Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement (CECA) of ASEAN and China came into effect on January 1, 2006.
ACFTA allows investors from China to engage in trade with Vietnamese partners and benefit from favorable import tariffs stated in the import tariff schedule. As per Decree 153/2017/ND-CP, the current special preferential tax schedule applies for the period of 2018-2022.
In addition to tax eliminations, Vietnam will also reduce import tax on sensitive products imported from China such as electric appliances and processed agricultural products to 5% by 2020.
#6 ASEAN-Korea Free Trade Area (AKFTA)
Vietnam, as a member state of ASEAN, also entered Free Trade Agreement with Korea in 2005.
Vietnam released the import tariff schedule for AKFTA in Decree 157/2017/ND-CP, effective from January 1, 2018. The current tariff table applies for the period of 2018-2022.
By 2018, Vietnam eliminated import taxes on 86% of all the products in the list and the new tariff schedule lifted import taxes on over 700 additional products.
#7 Vietnam-Chile Free Trade Agreement (VCFTA)
Vietnam and Chile have signed a Free Trade Agreement which took effect in January 2014. Unlike other Vietnam trade agreements that also target other economic activities, VCFTA only includes the trade of goods.
In accordance with the VCFTA, Vietnam will eliminate around 88% of tariff rates for 15 years starting from 2016, creating excellent opportunities for Chilean investors to explore and conduct business in the Vietnamese market.
#8 Vietnam-Japan Economic Partnership Agreement (VJEPA)
Vietnam and Japan signed the VJEPA in 2008, and it took effect in 2009.
Currently, the special preferential import tariff schedule for 2015-2019 is in force. It was announced in Circular No.25/2015/TT-BCT on February 14, 2015, and states tariff rates for each year separately, ultimately aiming to cut taxes on 90% of the products.
#9 Vietnam-Republic of Korea FTA (VKFTA)
In addition to AKFTA, Vietnam and the Republic of Korea have also signed a Vietnam-Korea Free Trade agreement. The latter provides more preferences on goods, services, and investments than AKFTA, including tax eliminations on products such as:
- Electronic components and automotive parts
- Textile and garment
- Electrical appliances
Also, note that the VKFTA does not replace the AKFTA; these two agreements are in effect simultaneously. Therefore, when planning to do business in Vietnam, Korean investors have the advantage of choosing the preferable agreement to take the maximum benefit from tax reductions.
#10 Vietnam-Eurasian Economic Union Free Trade Agreement
In May 2015, Vietnam and the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU) including Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, and Russia signed the Vietnam-Eurasian Economic Union Free Trade Agreement.
The agreement took effect in 2016, and Vietnam aims to reduce import tariffs on 90% of products.
This agreement eliminates tax on products such as:
- Agricultural commodities (immediately)
- Electrical and agricultural machinery (after 3-5 years from the enforcement of the agreement)
- Pork, chicken (after five years)
- Alcoholic beverages and cars (after ten years from the enforcement of the agreement)
#11 Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP)
The Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership was signed on March 8, 2018, and it took effect on January 14, 2019.
The agreement includes 11 members: Australia, Brunei, Canada, Chile, Japan, Malaysia, Mexico, New Zealand, Peru, Singapore, and Vietnam.
Participating countries agreed to remove almost all import duties according to schedule, creating more opportunities for small start-up businesses and more benefits for consumers and customers.
The CPTPP concerns:
- Tariff reductions for goods
- Service market opening
- Intellectual property
- Trade-related technical barriers
- Labor
- Environment
- Government procurement
- State enterprises
- Telecommunication
- Finance services
Source: Ministry of Finance of Vietnam
For more information about specific products or agreements, reach out to our consultants via [email protected].
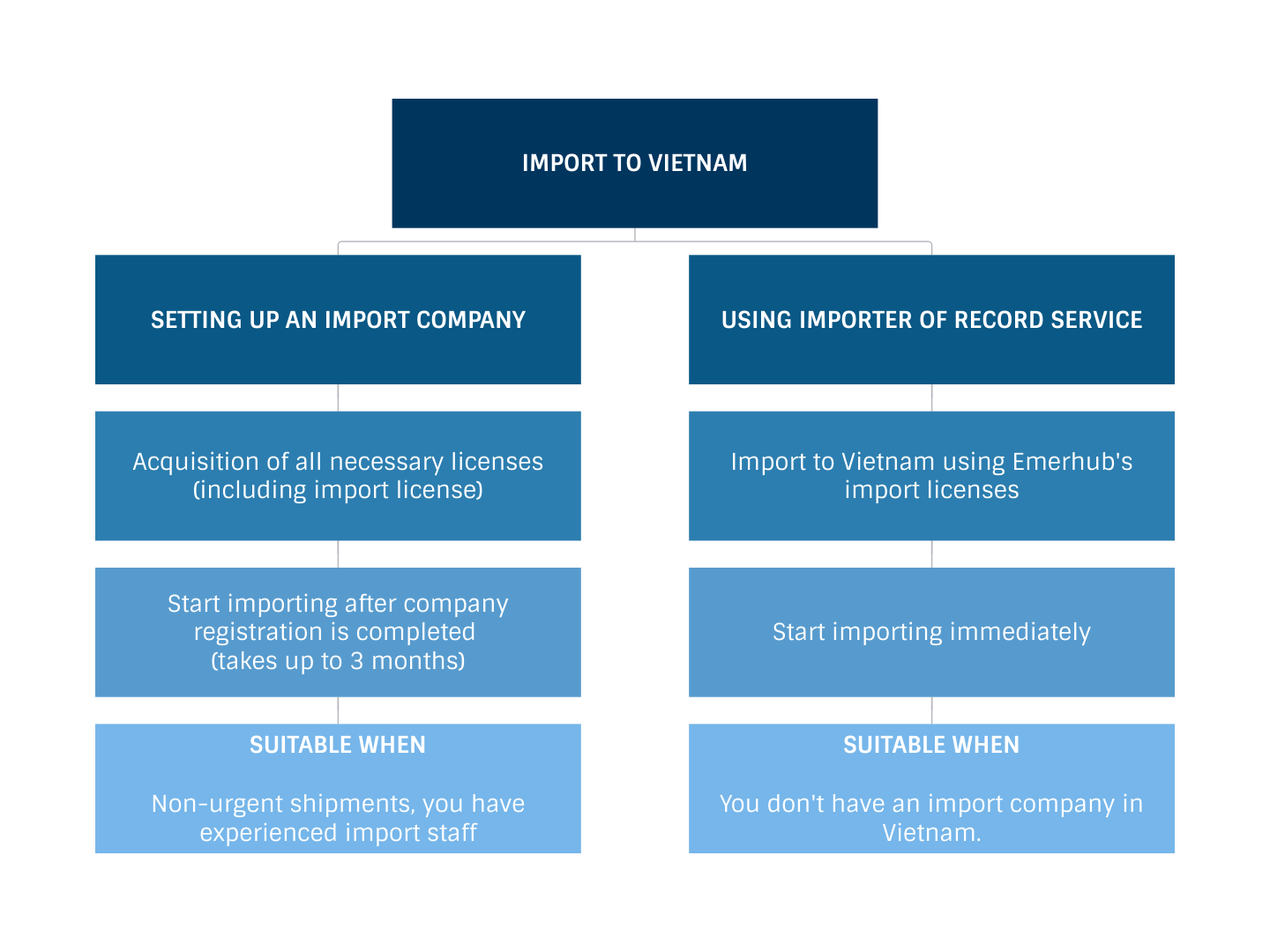
How to import to Vietnam
Setting up an import company in Vietnam
To start importing to Vietnam, you first have to register a company in Vietnam. During this process, you will also receive an import license among other necessary permits. Also, note that it can take up to 3 months to register a company in Vietnam.
However, when opting for your own import company, be sure to avoid common mistakes foreign investors are prone to make when setting up a company in Vietnam. For example, choosing the wrong amount of capital or not planning enough time for company registration.
Using importer of record service in Vietnam
Another alternative to company registration in Vietnam is to use an importer of record service. It is faster and also requires less hassle from your side. Find the benefits of using importer of record service in our previous article.
Want to learn more about Vietnam trade agreements or how to import to Vietnam? Get in touch with our consultants by filling in the form below.
Further reading: How to Calculate Import Tax in Vietnam (import tax calculator included)







