Table of contents
Vietnam’s GDP growth touched 8.02% in 2022 which is an increase of 2.58% YoY. With average annual GDP growth of more than 6% over the past two decades, Vietnam has become the top country with the highest growth in the SEA region. It is also attracting foreign investments due to its strategic location and its membership in 15 Free Trade Agreements (FTAs). However, import to Vietnam is still highly regulated by the government.
In this article, Emerhub is going to explain some of the key elements you need to know when planning to import to Vietnam.
Why import to Vietnam?
Quickly developing infrastructure
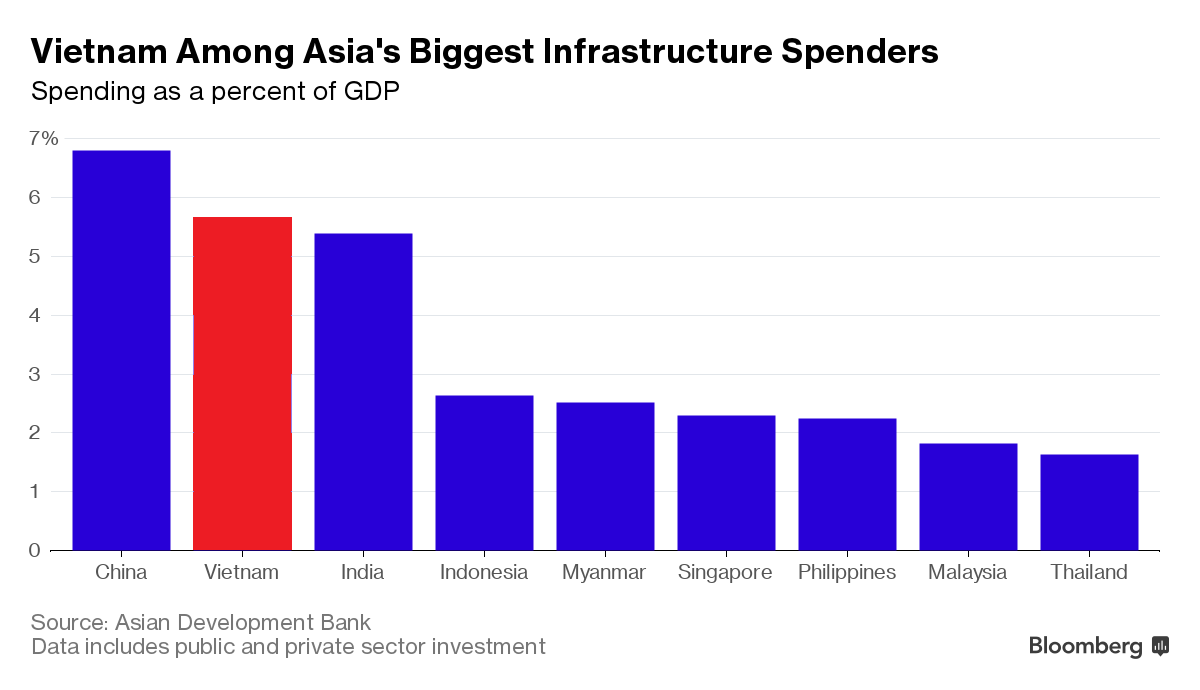
According to the Asian Development Bank, Vietnam invests nearly 6% of its GDP on infrastructure development which is almost double compared to other emerging markets in Southeast Asia.
Vietnam’s infrastructure quality is ranked 47th out of 160 countries according to the World Bank report. Efficient transport infrastructure leads to an increase in the speed of transportation, reducing the time and cost of importing goods into the country. Vietnam also has a comprehensive network of 251 ports with a collective capacity of 543.7 million tons of cargo per year. Quickly developing infrastructure is attracting foreign investors to set up manufacturing companies which, in turn, encourages the import/export sector.
Source: Bloomberg
Trade agreements and openness to foreign direct investment
Over the past 30 years, Vietnam is transforming itself into a globalized economy. The country is now a member of the World Trade Organization ( WTO) and is also a part of numerous international partnerships, including 15 free trade agreements and 2 negotiating FTAs with partners both within and outside the region.
Additionally, Vietnam offers several tax incentives to foreign investors. For example, investors who contribute to specific geographical regions or sectors of particular interest, such as high-tech or health care, can enjoy some tax benefits.
The growing digital economy in Southeast Asia
Vietnam’s digital economy reached an estimated value of 23 billion USD in 2022. It is a remarkable surge of 28% from the previous year, which is the highest growth rate among all the countries in the region.
Furthermore, data released by the Ministry of Information and Communications indicates that the revenue generated by Vietnam’s digital economy has also experienced a substantial increase. In 2022, the revenue generated in this sector surpassed 148 billion USD, representing a notable rise of over 10% from the preceding year. The growth in demand for digital products and services such as software, and electronics has led to an increase in imports of these goods into Vietnam.
Increasing consumer class
Over the past two decades, the consumer class in Vietnam has expanded dramatically. Vietnam is poised to add 36 million people to its consumer class by 2030, further accelerating its upward trajectory.
Luxury brands like Chanel, Versace, and Armani are opening stores in Saigon due to Vietnam’s expanding consumer class. The middle class, responsible for over 50% of the country’s consumption, offers significant purchasing power that attracts foreign brands. Importing luxury goods into Vietnam is now a lucrative opportunity for businesses.
Find out more: Top 12 Reasons to Invest in Vietnam
Understanding Vietnam import regulations
Licenses for importing to Vietnam
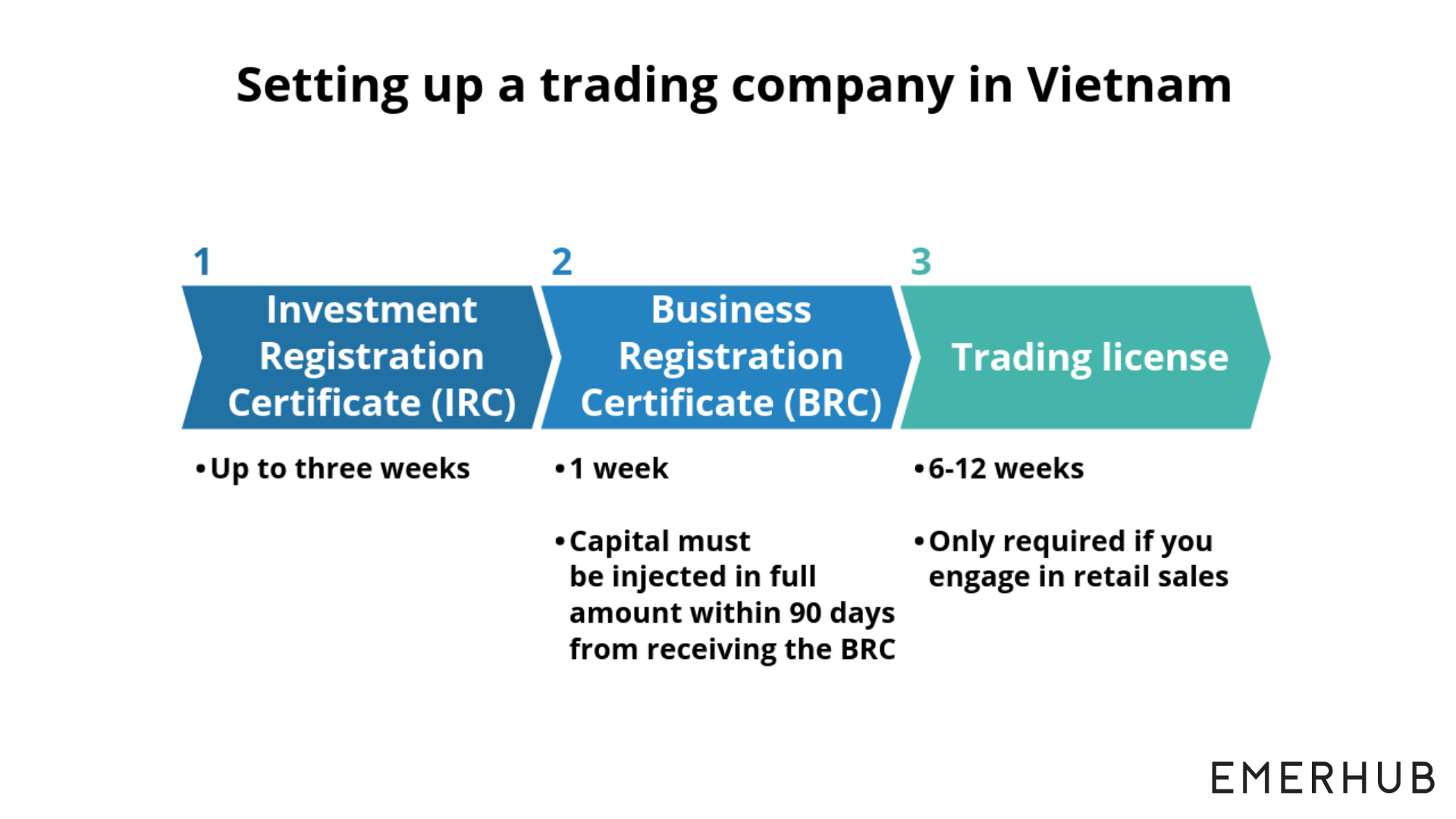
To import in Vietnam, you need to obtain an investment license (IRC) and a Business Registration Certificate (BRC) from the Department of Planning and Investment (DPI).
There is no separate import license in Vietnam, the investment license allows you to import and/or export products. You also don’t need additional licenses if you are planning to wholesale your goods to businesses (B2B).
However, to sell your products directly to consumers (B2C) you need a retail license. It takes 6-12 weeks to obtain a retail trading license, and you can apply for it after the incorporation, once you have paid the capital contribution.
Keep in mind that you need to know the products you are planning to import before applying for BRC and IRC. If the company wants to import additional products in the future, you have to change your license.
Product registration in Vietnam
Certain products are required to be registered before importing. For example, cosmetic products must first be registered with the Drug Administration of Vietnam before any trading can take place.
Other products that are subject to registration are:
- drugs and food supplements
- processed products from vegetables, fruit, grain
- wine and cigarettes
- essential oils, perfumes, cosmetics
- milk and dairy products, eggs, honey, and other animal-derived products.
Emerhub handles both the incorporation and product registration process.
Import taxes in Vietnam
Most goods imported to Vietnam are subject to duty. Imported products are subject to import tax and value-added tax (0%, 5%, or 10%). Tax rates vary depending on the type of product.
For example, consumer goods, especially luxury goods are usually subject to higher tax rates than machinery, raw materials, or equipment used in production.
However, Vietnam is a member of over 15 ASEAN Free Trade Areas, and intra-regional import taxes for certain products range from 0-5%, including products such as:
- livestock
- meat and fish
- fruit and vegetables
- medicaments and pharmaceutical goods
- agricultural machinery
To demonstrate the import tax calculation, we have provided some simple formulas and illustrative examples in our article on how to calculate import tax and duty in Vietnam.
Prohibited products
Circular No. 34/2013/TT-BCT of the Ministry of Industry and Trade brings out a list of products that foreign capital companies cannot export from, or import into, Vietnam.
For example, some of the products that you cannot import to Vietnam include:
- cigars
- tobacco
- petroleum oils
- newspapers and journals
- second-hand items (including electronics and automotive)
How to import to Vietnam?
To import to Vietnam, you must have a legal entity registered in Vietnam or a partner/receiver who has a legal entity in Vietnam. Therefore, you have two options for importing to Vietnam.
Option 1: Set up a trading company in Vietnam
In general, it takes one month to register a company in Vietnam. If you also want to sell the products you import to Vietnam then you need a retail trading license which takes 6-12 weeks to acquire.
However, note that you can already start importing your products once your company is registered.
In general, there is no minimum capital requirement for setting up a trading company in Vietnam. However, the capital you inject must comply with your planned expenses.
Emerhub can assist you in establishing a company in Vietnam. We will take care of all the paperwork and communicate with the authorities on your behalf.
Learn more about the cost of company registration in Vietnam
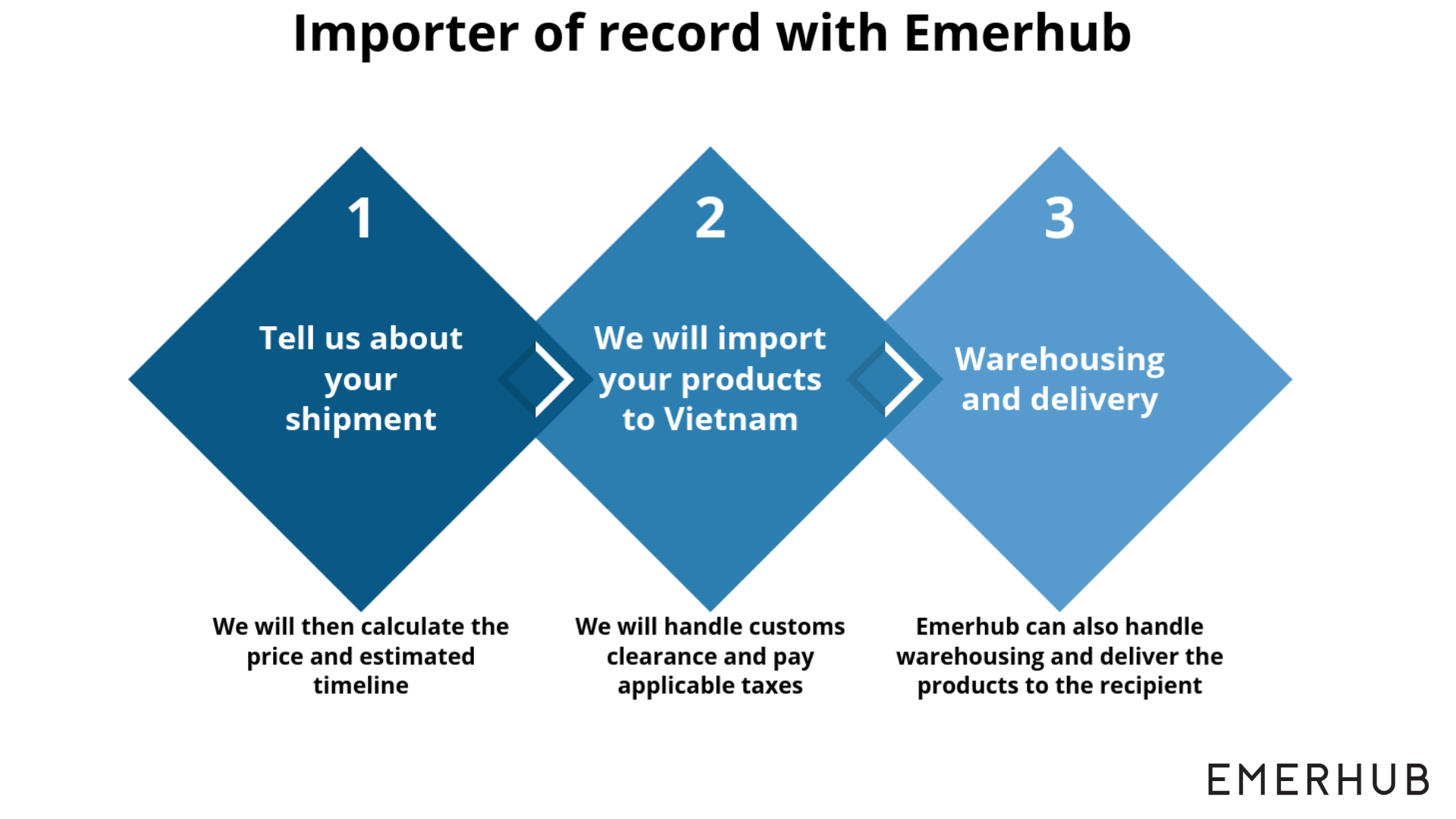
Option 2: Import to Vietnam using an importer of record
If you don’t want to set up a legal entity in Vietnam or wish to test the market by importing a few shipments, you can use an Importer of Record instead.
What is an importer of record (IOR)?
Importing to Vietnam using an importer of record means that you don’t have to acquire any import licenses or set up a company in Vietnam. Furthermore, with an IOR you can start importing immediately.
Among other benefits of using the importer of record service, you are also exempt from tax liabilities since we will cover the taxes.
Using a nominee registrar
As already mentioned, some imported products require registration.
Emerhub can also act as your nominee registrar. In that case, Emerhub will make the announcement/registration of the product and share it with the importer for customs clearance.
Get in touch today to get started.
Popular products to import into Vietnam
Many sectors rely heavily on imported goods. According to the General Statistics Office of Vietnam, the import turnover of goods reached an estimated $360.65 billion, an increase of 8.4% YoY; the area with foreign investment reached $234.86 billion, an increase of 7.5%. In 2022, 09 imported items with a value of over $10 billion, and the top 5 are:
- Computers, electrical machinery, and equipment
- Telephones, mobile phones
- Iron and steel
- Fabrics
- Plastic materials
At the same time, we see a shift in the Vietnamese market structure, taking the lead as a manufacturing country due to an increase in the skilled and cheaper labor force compared to China. Additionally, this increases the demand for raw materials and technical and electrical machinery.
Vietnam’s biggest trade partners
According to the General Department of Vietnam Customs, Vietnam’s main import partners in 2022 were:
|
Country |
Value in US$ (percentage of total imports) |
| 1. China |
117.95 billion (7.7%) |
| 2. South Korea |
62.09 billion (10.5%) |
| 3. United States |
14.47 billion (5.2%) |
| 4. Japan |
23.37 billion (2.3%) |
Products with the most complicated import regulations
While some products, such as medical devices, can be imported to Vietnam quite easily, others can be listed as complicated products.
For example, products such as:
- cosmetics
- telecommunication items
- animal feed
- health supplements
These are goods that either require additional licenses or for which the Ministry of Trade only gives out a limited amount of import licenses.
Obtaining the necessary licenses for these products is not impossible, but, in some cases getting your hands on the license or outstanding local distributor may turn out to be more expensive, time-consuming, and complicated than originally anticipated.
However, stricter regulations also make the competition weaker, and Emerhub can handle the process of product registration on your behalf.
Ready to start importing to Vietnam?
Leave your details in the form below for a complimentary consultation. Our consultants are happy to help you import your products to Vietnam.